As we all know, China's automobile industry is developing rapidly. In 2009, China's automobile industry overcame many difficulties brought about by the world financial crisis and achieved good results. Both automobile production and sales exceeded 13 million. It can be expected that China's automobile industry will maintain a rapid development momentum, and the demand for various spare parts required for automobile assembly will also increase. How to improve the quality of products while increasing production, and to consider energy conservation, consumption reduction, and environmental protection have become issues that must be faced and considered by various auto parts manufacturers.
At present, surface heat treatment methods widely used in China mainly include carburizing, nitriding and carbonitriding. The quenching is carried out by using a conventional carburizing furnace. Due to the long time consuming, the workpiece is often deformed in a large amount, and the energy consumption is high and the efficiency is low. With the development of science and technology, induction heating technology is increasingly applied to the heat treatment of metal surfaces. Nowadays, the latest SDF synchronous dual-frequency induction heating technology makes energy-saving, consumption-reducing and environmentally friendly surface heat treatment methods possible.
Despite the many challenges, we still hope to find a production model that is more efficient and yields. The “green production†approach requires consideration of the entire process, from product development to process technology, as well as energy and materials. Based on many decisions on cost, performance and quality, “Green Production†uses many economical solutions to effectively reduce costs, save energy and protect the environment.
First, the development, characteristics and advantages of SDF® synchronous dual-frequency induction heating technology
1. Single frequency induction heating confusion
It is well known that compared with other conventional heat treatment methods, induction hardening has high surface hardness, low brittleness, high fatigue strength, good surface quality of the workpiece (not easy to oxidize and decarburize), small deformation, heating temperature, depth of hardened layer, etc. The parameters are easy to control and so on. However, for a workpiece having a concave-convex surface structure like a gear, conventional single-frequency induction heating technology cannot achieve satisfactory processing results.
Since the gear has a convex surface and a concave surface, the surface of the gear is quenched by high-frequency induction heating (see Fig. 1), the heat generated by the induced current is rapidly transmitted, the tooth top is completely hardened, but the root hardening is insufficient. In addition, this treatment method tends to increase the residual stress on the root tooth surface, resulting in the occurrence of fracture. 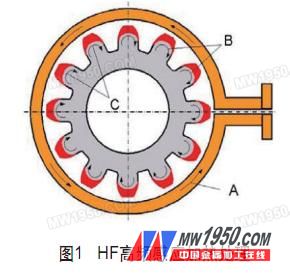
Similarly, medium-frequency induction heating is used for surface quenching of the gear (see Figure 2). Heat is conducted at the root. Due to the concave shape of the root, heat is exponentially decreasing during conduction, and the root is effectively hardened. The top of the tooth is not hardened. 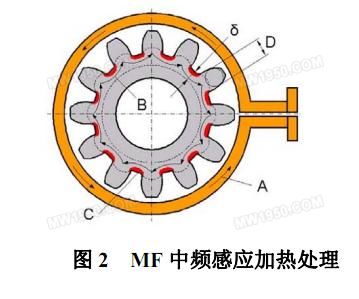
How to effectively avoid this phenomenon? It turns out that it is impossible to achieve such a processing task by using single-frequency induction heating; if the root and the top of the gear are separately treated by induction heating with different frequencies, the contour hardening effect of the gear is often unbalanced. The use of synchronous dual-frequency induction heating technology, the same induction coil simultaneously outputs two frequencies for heat treatment, this problem is solved. 1 2 Next page