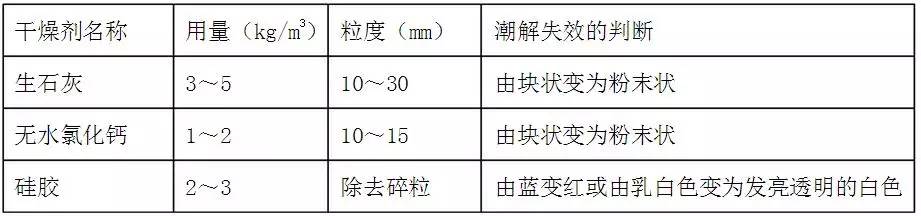
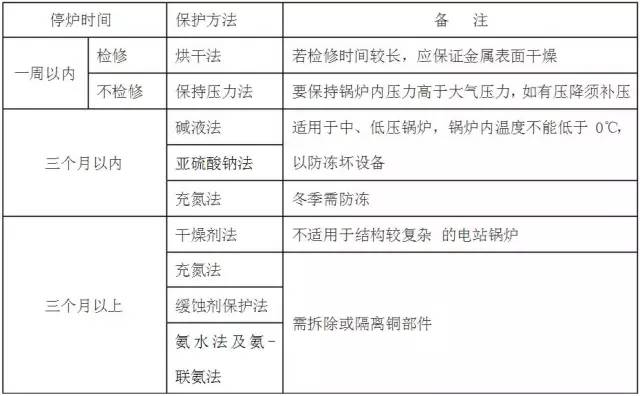
Deactivate boiler corrosion If the boiler does not take appropriate protective measures during the decommissioning, the body of the boiler and the entire soda system Metal surfaces are subject to corrosion by dissolved oxygen and are attacked much faster than during operation. It turns out that most of the seriously corroded boilers are caused by improper shutdown protection, and if these corrosion products are not removed, they will accelerate electrochemical corrosion after the boiler is re-run. Therefore, shutdown corrosion will not only shorten the service life of the boiler, but also create operational hazards. After the boiler is deactivated, a large amount of outside air will enter the boiler's soda system. Especially when the boiler is not cooled after cooling, a metal film will adhere to the metal surface, and the oxygen in the air will dissolve in the water film. After reaching saturation and oxygen and iron corrosive reaction, the oxygen in the air will be quickly and continuously replenished, so it is easy to cause oxygen corrosion of the metal. If the furnace water remaining on the metal surface contains Cl- or SO42-, the corrosion will be more serious. The extent of corrosion that occurs during shutdown is related to a variety of factors. It mainly has the following points: 1, humidity For boilers with water release, the moisture on the metal surface has a great influence on the corrosion rate. When the air humidity is high, it is easy to dew on the metal surface to form a water film, which causes corrosion to increase. When the metal surface is dry and the relative humidity inside the boiler is less than 30%, the corrosion of iron can be completely prevented. 2. Salt content in water An increase in the salt content in the boiler or in the water film on the metal surface accelerates the corrosion, especially when the oxide and sulfate contents increase, the corrosion rate will increase significantly. 3, the degree of cleanliness of the metal surface When there is sediment or water slag on the surface of the metal, the part tends to accumulate residual moisture, so that the metal surface under the slag is always in a wet state, and the slag prevents the oxygen from diffusing in, and the metal surface around the slag is more Sufficient oxygen. Thus, due to the difference in the concentration of the nutrient, a concentrated corrosion battery is formed, and the portion where the oxygen concentration around the slag is large is the cathode, and the portion where the oxygen concentration is low under the slag is the anode, and the metal under the scale is corroded. It can be seen from the above that in order to prevent the corrosion of the boiler from being stopped, the metal surface of the boiler should be kept dry and clean, and the scale or accumulated water slag should be removed in time; for wet protection, the salt content in the water should be reduced as much as possible to prevent acceleration. Oxygen corrosion. 1. Prevent outside air from entering the deactivated boiler soda system; 2. Keep the metal surface in the soda system dry; 3. Form a film with anti-corrosion effect on the inner surface of the metal to insulate the air; 4. Soak the metal surface in a medium containing an oxygen scavenger or other protective agent. Dry protection and wet protection The desiccant method is suitable for boiler protection with a longer shutdown time (more than three months). For boilers with a larger drum volume occupying the entire boiler water volume ratio, the more convenient this method is. The specific method is as follows: (1) After the waste heat boiler is deactivated, the boiler should be shut down for maintenance. When the boiler inlet temperature drops below 300 °C and the furnace water temperature drops to about 100 °C, the sewage doors are opened to completely exhaust the boiler water in the waste heat boiler. Open the inspection holes, remove the scale and slag deposited in the boiler, and the external soot. Use the waste heat of the kiln to dry the heating surfaces and equipment of the boiler, and then close the valves of the boiler after drying. (2) Put the desiccant into the steam drum and each joint box (the position and quantity of the desiccant to be placed should be recorded to prevent forgetting). Immediately after the insertion, the steamer manhole door and each steam water valve are closed to make the steam water system tightly isolated from the outside air. Desiccant dosage and failure judgment (3), pay attention to the following issues when desiccant maintenance: The desiccant should not directly contact the surface of the boiler metal, and can be installed in a container such as an iron plate; After placing the desiccant, the hand hole and other hole cover should be closed, and the valves on the steam and water pipes must be cut off; The desiccant should be inspected regularly. Generally, the desiccant should be inspected once every half month or so. The desiccant should be inspected every 1 month, and the failure should be replaced in time. The drying method is often used for anti-corrosion during boiler maintenance. When the temperature of the furnace water drops to about 100 °C, the boiler water is completely exhausted, and the surface of the boiler metal is dried by the residual heat of the furnace. The ammonia filling method is generally used for the protection of long-term shutdown of power station boilers. Since ammonia has a corrosive effect on copper, all copper components in the boiler soda system should be removed or plugged and isolated when the ammonia charging method is used. The ammonia filling method is to charge the boiler with ammonia after the boiler is deactivated, so that the ammonia pressure in the boiler is maintained at 13kpa to discharge the air and reduce the oxygen content in the water film on the metal surface. Since the ammonia gas is dissolved in the water film, the metal surface can have good corrosion resistance. Therefore, the ammonia filling method does not have strict requirements on the dryness of the metal surface, but the entire system must be tight and leak-free. The wet red litmus paper is used to check the possible leakage of ammonia gas. If the test paper changes from red to blue, ammonia gas leaks and the leak is immediately blocked. Open fire operations should also be strictly prohibited to prevent explosions. Corrosion inhibitors for shutdown protection generally have good volatility and are therefore also referred to as vapor phase corrosion inhibitor processes. The main corrosion inhibitors are: inorganic ammonium salts such as ammonium carbonate, ammonium hydrogencarbonate and diammonium hydrogen phosphate, organic amines such as cyclohexylamine, urotropine and benzoic acid, and composite TH901 corrosion inhibitors. The characteristics of this kind of corrosion inhibitor are: volatile, can form a certain vapor pressure; can form a protective film on the metal surface, have high anti-corrosion ability; the dryness of the metal surface is not high, especially the TH901 corrosion inhibitor It also has a good anti-corrosion effect on wet metal surfaces. Instructions: After the boiler is drained, the slag is removed, and the medicament is evenly distributed in the furnace according to a certain amount of proportion. The valves are closed and the system is tightly sealed. It should be noted that most of these corrosion inhibitors will volatilize ammonia and have an erosive effect on copper parts. Therefore, all copper components in the boiler soda system should be removed or plugged off; or ubiquitin: benzotriazole: cyclohexylamine = 3:2:7 (mass ratio) mixed corrosion inhibitor To prevent corrosion of copper parts. Wet protection refers to a method of filling a boiler with a protective aqueous solution during shutdown to prevent air from being subjected to a system of protection. It can be divided into the following types: That is, the method of adding alkali solution is used to fill the boiler with an aqueous solution having a pH of more than 10 to passivate the metal surface to prevent corrosion of the metal by dissolved oxygen. A mixture of sodium hydroxide and trisodium phosphate is often used, and the method can be used within three months of shutdown time. (1) After stopping the furnace, first remove the dirt and water slag inside and outside the boiler, and block the pipeline connected to the outside; remove all copper components in the steam water system or block the isolation. (2), add sodium hydroxide (dosage: 4kg / m3) and trisodium phosphate (dosage: 1.5kg / m3) dissolved in demineralized water or condensed water, then added to the boiler, and use a pump to circulate the alkaline solution in the boiler Evenly. (3) It is preferable to heat the furnace water to about 105 ° C to remove oxygen and other gases in the water. Then close all door holes and valves and keep them free of leaks. If the boiler has a short outage (within one week), the boiler can be pressurized and maintained. The small-capacity boiler can use the residual pressure of the boiler (0.05~0.1MPa) to keep the boiler water temperature slightly higher than 100°C; The medium and high pressure boilers can be filled with qualified feed water in the boiler, and the pressure of the feed water pump is used to maintain the boiler pressure at about 0.5 to 1.0 MPa. Close all valves in the soda system to prevent air from entering the boiler. In order to maintain the pressure and temperature of the boiler, it is possible to periodically generate a slight fire under the kiln evaporator, or to periodically heat the boiler steam of the adjacent kiln. If the pressure of the boiler is found to drop, the cause should be ascertained and the pump should be pressed to the specified pressure. Sodium sulfite is a reducing agent that reacts well with oxygen in an alkaline solution to prevent corrosion of the metal by oxygen. The method is to add sodium sulfite on the basis of the lye method. It is generally required to maintain an excess of sodium sulfite in water of 10 to 30 mg/L. This method is used when the boiler is out of service for a long time. After the boiler is deactivated, the furnace water is drained, the copper parts in the system are removed or isolated, and the ammonia solution with a concentration of 700-800 mg/L prepared with condensed water or feed water is charged; or the water is not discharged after the boiler is deactivated, directly charged. Ammonia and hydrazine. The pH of the water in the boiler is between 10 and 10.5, and the excess of hydrazine should be 200 mg/L. The liquid medicine is pumped into the system and circulated to uniformity. After the boiler is evenly filled with the protective liquid, the valves are closed. The entire system should be tight and leak-free during shutdown to prevent air ingress. In this way, when the boiler is to be put back into operation, the protective fluid should be completely drained and thoroughly rinsed. After ignition, the steam should be exhausted from the empty exhaust valve until the ammonia content in the steam is less than 2 mg/kg, so that the steam can be sent to avoid excessive corrosion of the condenser copper tube. The boiler nitrogen charging method can be carried out without the wet water method or the empty boiler dry method. Because nitrogen is very inactive and non-corrosive, it can prevent oxygen from entering when the boiler is filled with a certain pressure of nitrogen. For boilers with complicated structure, some parts of the water are not easy to put clean, it is not suitable to use dry maintenance, you can use nitrogen filling method. The method is as follows: before the furnace is shut down, the nitrogen-filled pipeline is connected. When the pressure of the boiler is reduced to about 0.15 Mpa, the nitrogen gas is supplied to the boiler steam drum and the economizer through the temporary pipeline through the nitrogen pipeline. Specific requirements are as follows: (1) The purity of nitrogen is above 99%; (2) When the empty boiler is filled with nitrogen, the nitrogen pressure in the pot should be above 0.15Mpa; before the wet method is filled with nitrogen, it is better to add an appropriate amount of hydrazine in the boiler, and adjust the pH value of the boiler water to 10 or more with ammonia water; (3) When filling nitrogen, all valves in the boiler steam water system should be closed, and the boiler should be kept tight and not leaked; if there is leakage, it will be eliminated immediately, so as to avoid excessive consumption of nitrogen due to leakage and difficulty in maintaining nitrogen pressure. The protection of the boiler shall be selected according to the boiler structure, deactivation time and anti-corrosion requirements. The above protection methods are summarized in the following table for reference: Kitchen Shower,Kitchen Faucet,Brass Kitchen Faucet,Pull Down Kitchen Faucet Yuyao Zelin Sanitary Ware Co., Ltd , https://www.kitchen-sinkfaucet.com